Seal whiskers, the secret weapon for hunting
- Headline
- Press Release
Researchers study elephant seal whiskers and their role in the sensing prey
The deep ocean is a dark place, yet deep-diving seals can easily locate their prey in that darkness. A multi-national research team has used field-based studies to better understand how seals use their whiskers in their search for prey.
The team published their findings in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science.
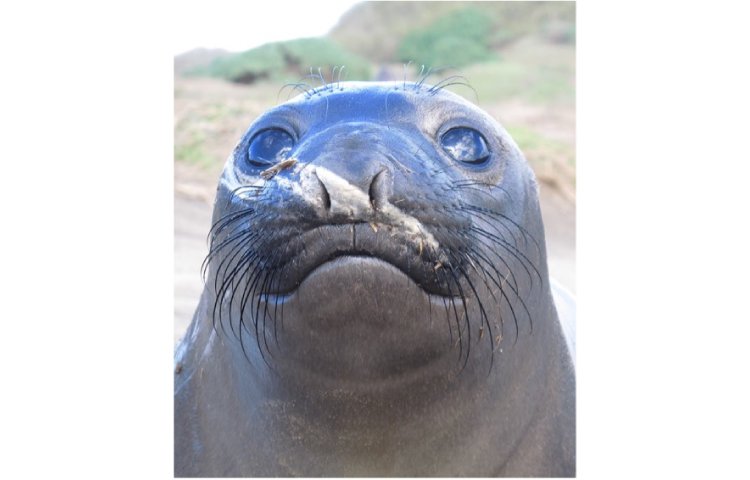
Elephant seal whiskers. Northern elephant seals have highly developed whiskers. Photo shows a weaned elephant seal during breeding season (February) at Año Nuevo State Park, CA, USA (NMFS#23188). Credit: Photo taken by Taiki Adachi.
In deep ocean waters where no sunlight reaches, bioluminescence, the light that some creatures carry in their bodies, provides light. But this light from bioluminescence is very limited. Toothed whales are able to hunt in these dark waters, using active biosonar, or echolocation, to find their prey. Deep-diving seals hunt in these waters too. Yet they lack the active sonar the whales have to help them hunt.
The team hypothesized that the seals rely on their highly-developed whiskers to locate prey.
Unlike humans, most mammals have vibrissae, or mobile facial whiskers. The word "vibrissae" comes from the Latin word "vibrio" which means "to vibrate." Used to describe the seals' whiskers, it stresses the reception of vibration information. Until now, researchers have not understood the natural movement and function of mammals' facial whiskers because of the challenges in observing the whisker movement in a mammals' natural environment.
Previous studies had been conducted in experimental settings with isolated whiskers, artificial models, or captive animals. The team wanted to learn how the seals used their whiskers in their natural deep ocean environment. The researchers placed small video loggers on free-ranging female northern elephant seals, choosing elephant seals because of their highly sensitive whiskers. These seals have the highest number of nerve fibers per whisker of any mammal. The researchers mounted the video loggers on each seal's cheek to observe how the seal moves and uses the whiskers in front of its mouth.
With the video loggers, the researchers observed the elephants seal foraging in the extreme environment of the deep, dark ocean. The video logger was equipped with an LED red/infrared-light flash. This light was not visible to the seal, but it allowed the researchers to non-invasively observe how the seals use their whisker as they approach their prey. The cameras showed that the seals captured moving prey by sensing the water movement. With their whiskers extended forward ahead of their mouth, the seals performed rhythmic whisker movement--protracting and retracting their whiskers--to search for hydrodynamic cues, similar to the ways a terrestrial mammal explores its environment.
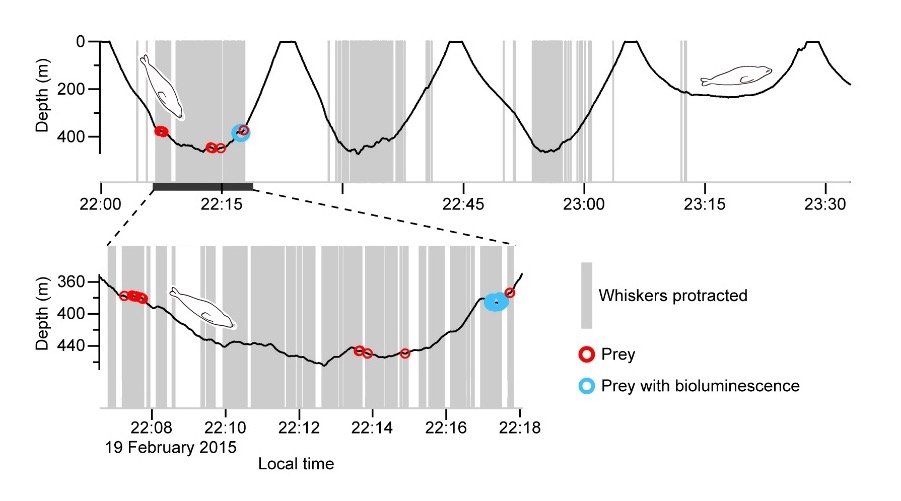 Time-series data of Seal. Elephant seals protract whiskers at deeper than 200 m depth, where they mainly forage and small fish (e.g. myctophid) is abundant. Credit: Taiki Adachi et al. (2022)
Time-series data of Seal. Elephant seals protract whiskers at deeper than 200 m depth, where they mainly forage and small fish (e.g. myctophid) is abundant. Credit: Taiki Adachi et al. (2022)
The team took into consideration the possibility that light provided by the bioluminescence in some prey might help the seals in their hunt for food. But their findings reveal that while bioluminescence is important, the seals' sensitive whiskers are the primary method the mammal uses to find its prey.
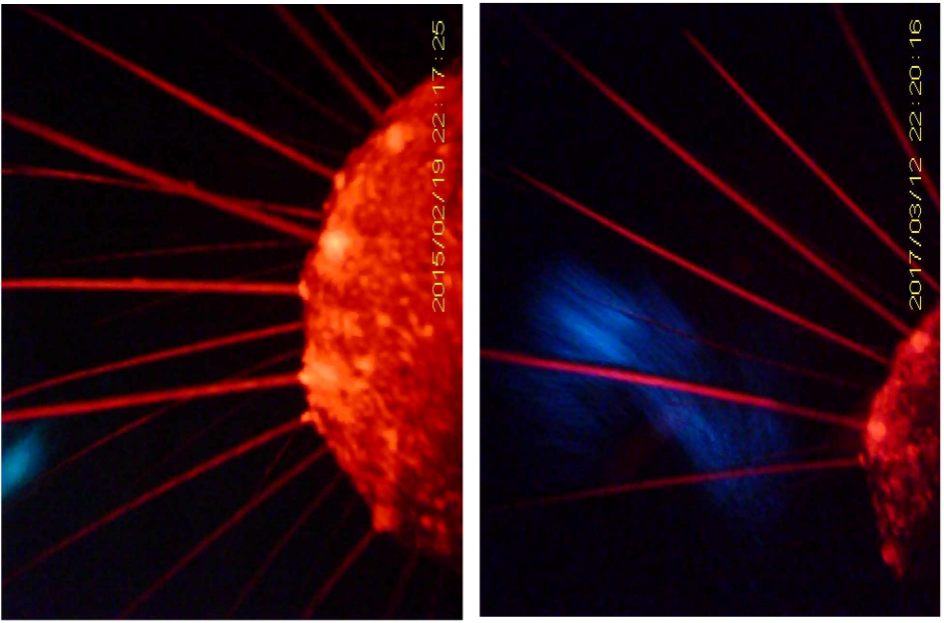 Elephant seal whiskers sensing prey with bioluminescence. Researchers from Japan studied the sensor function of elephant seal whiskers in hunting. Credit: Taiki Adachi et al.(2022)
Elephant seal whiskers sensing prey with bioluminescence. Researchers from Japan studied the sensor function of elephant seal whiskers in hunting. Credit: Taiki Adachi et al.(2022)
The seals' whiskers allow them to search for, pursue, and capture prey. "Our findings solve a decades-long mystery about how deep-diving seals locate their prey without the biosonar used by whales, revealing another mammalian adaptation to complete darkness," said Taiki Adachi, Project Researcher at the National Institute of Polar Research / Assistant Project Scientist of University of California Santa Cruz. This research complements earlier whisker studies conducted on mammals in captive conditions, and it propels forward the field of sensory ecology of foraging. "The next step is conducting comparative field studies on other mammals to better understand how whisker-sensing shapes natural behavior in each mammalian species under different environments," said Adachi.
Original article:
Journal: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of United States of America (PNAS)
Title: Whiskers as hydrodynamic prey sensors in foraging seals
Authors:
Taiki Adachi (National Institute of Polar Research; The University of Tokyo; University of St Andrews; University of California Santa Cruz)
Yasuhiko Naito (National Institute of Polar Research)
Patrick W. Robinson (University of California Santa Cruz)
Daniel P. Costa (University of California Santa Cruz)
Luis A. Hückstädt (University of California Santa Cruz; University of Exeter)
Rachel R. Holser (University of California Santa Cruz)
Wataru Iwasaki (The University of Tokyo)
Akinori Takahashi (National Institute of Polar Research; The Graduate University for Advanced Studies (SOKENDAI))
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2119502119
URL: https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2119502119
Available Online: Available Online: June 13, 2022